
Quality Treatment With Super Affordable Price
Best Physiotherapy Treatment India
Call us anytime
Write a mail
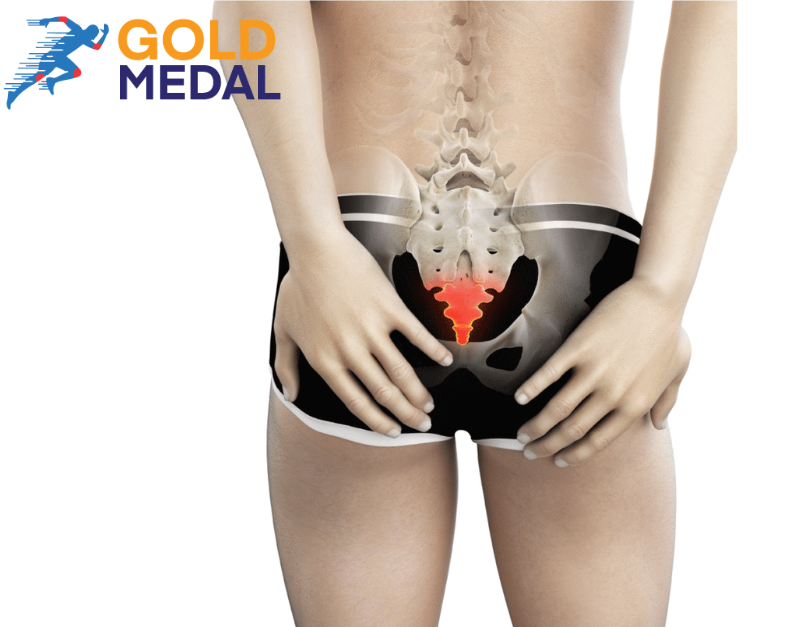
Routine activities can become intolerable or at least uncomfortable if there is coccydynia or pain in the tailbone. At the spinal column’s base is a small, triangular bone called the coccyx that is vulnerable to bruising and even fracture. Walking eases pain, whereas sitting makes it worse. Utilizing natural remedies and changing bad habits, like spending too much time sitting down, will result in the biggest changes. What is Coccydynia? Pain in and around the tiny triangular bone at the base of your spinal column, above the cleft in your buttocks, is called coccydynia or “tailbone pain.” The word “coccyx” is derived from the Greek word for “cuckoo” because it has a downward-pointing beak-like tip. Coccydynia is the medical term for pain in the coccyx, and “Gdynia” is the Greek word for pain. Because it is situated where an animal’s tail would be, the bone is called the “tailbone.” Your coccyx comprises three to five fused vertebrae (bones). It is situated below the sacrum at the base of your spine. Numerous tendons, muscles, and ligaments affix to it. The two bones that make up the bottom of your pelvis—the coccyx and the ischial tuberosities—support your weight when you sit down. Two-thirds of adults have a slightly curved coccyx rather than one that points downward, but an excessively curved coccyx is abnormal and painful. Causes Falling Who has yet to fall to their behind while tripping over? It is possible that the ice caused you to lose your balance. You might have dropped from a ladder. Or perhaps you sat too far back in your office chair and slipped and fell. If you fall hard, your tailbone (coccyx) may be fractured, dislocated, or left with bruising. Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI) While engaging in activities like rowing and cycling, you must sway back and forth to stretch your spine. If that motion is performed too often, the tissues surrounding your coccyx may become strained. Pregnancy/Childbirth A woman’s body produces hormones during the third trimester of pregnancy that soften the region between the sacrum and the coccyx. The coccyx can therefore move as needed during childbirth. While this is a typical process, the movement may unnecessarily stretch the muscles and ligaments surrounding the coccyx, increasing pain. The stress placed on these soft tissues prevents them from supporting your coccyx at the proper angle. Obesity The added weight puts more pressure on the coccyx. The coccyx may consequently lean backward. It will hurt if your tailbone is out of alignment. Underweight The coccyx may rub against the muscles, ligaments, and tendons if there is not enough fat in the buttocks to prevent this. The rubbing causes inflammation of the soft tissues. Sitting Simply doing this can make coccyx pain worse, especially if you are sitting on something hard or restricted. Do your best to get up often, stretch, and take short walks. Use a padded seat, or find a softer, more comfortable place to sit. Cancer Pain in the tailbone is a rare indication of cancer. It is extremely unlikely. Symptoms The following are examples of coccydynia symptoms: The following are additional coccydynia-related symptoms and signs: How does physical therapy help with tailbone pain? The coccyx, also called the “tailbone,” is the last segment of the vertebral column. Coccydynia is an uncomfortable condition that appears in/around the coccyx. This type of pain frequently starts when someone sits down suddenly or gets up from their seat after a while seated. This condition, also known as coccygodynia, can make life less enjoyable for a person. In addition to the buttocks, lumbar spine, and thighs, the pain, frequently described as “stabbing” or “piercing,” can also occasionally radiate to those areas. The coccyx is the final section of the vertebral column. By fusion, the vertebral units are joined. At the front of the coccyx, the muscles and ligaments that regulate the pelvic floor’s movements come together. The coccyx also serves as a support for the anus. Physiotherapy Approach to Improve The main goal of physiotherapy treatment is postural education. When sitting correctly, the thighs and ischial tuberosities bear the weight rather than the coccyx. Physiotherapists may also suggest using cushions. Coccygeal cushions, modified wedge-shaped cushions, help to lessen the pressure that sitting has on the coccyx. Other types of treatment consist of: Mobilizations It might help to correct the posture of the coccyx. Mobilization techniques may be the most effective when increasing coccygeal mobility is the treatment objective. Manipulation Patients may benefit from having their coccyx manually adjusted. The coccyx-sacrum joint can be manually adjusted to help relieve pain brought on by coccyx mobility restrictions. Massage Coccydynia can be treated or lessened by massaging the tight pelvic floor muscles attached to the coccyx. The ligaments and sacrococcygeal joint can become more stressed due to tense muscles in this region, which can also pull on the coccyx and limit mobility. TENS unit By electrically stimulating the skin, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulator (TENS) devices shield the brain from receiving pain signals from the coccyx. These devices might be a good choice for patients who want to take the fewest medications possible. Dry needling For conditions like pelvic pain, incontinence, coccyx pain (tailbone), and other diagnoses, it is surprisingly comfortable and highly effective. It evaluates the mobility and position of the sacrococcygeal joint as well as helps to lessen muscle spasms. Simple Ways To Prevent Tailbone Pain Reduce your likelihood of developing tailbone pain by: Gold Medal Physiotherapy is best if you are searching for the best Coccydinia or Tailbone therapy. For more details about our doctors, you should visit the Gold Medal Physiotherapy website.

The leading cause of chondromalacia patellae, also referred to as “runner’s knee,” is the softening of the cartilage in the kneecap. Although older adults with knee arthritis may also experience it, young athletes frequently do. Chondromalacia is frequently regarded as an overuse injury in sports, so taking a few days off from training is occasionally beneficial. In other cases, poor knee alignment is to blame, and resting is ineffective. Runner’s knee symptoms include knee pain and a grinding sensation, but many patients never go to the doctor. Definition of Chondromalacia Patella Chondromalacia patellae (CMP) is a condition that causes structural and biomechanical changes that cause anterior knee pain. Sclerosis of the underlying bone and softening, swelling, fraying, and erosion of the hyaline cartilage beneath the patella are symptoms of degenerative changes occurring in the articular cartilage on the posterior surface of the patella. Chondromalacia patellae is one of the most frequently occurring causes of anterior knee pain in young people. It can affect up to one in four people, making it the most common cause of death in the US. The word “chondromalacia” combines the Greek words Chronos, which means cartilage, and malaria, which means softening. Consequently, chondromalacia patellae is a softening of the articular cartilage on the patella’s posterior surface, which may eventually lead to fibrillation, fissuring, and erosion. Additional diagnoses of chondromalacia include patellofemoral pain syndrome and patellar tendinopathy. Chondromalacia is not thought to be a part of PFPS in general. Since it is thought that the pathophysiology is different, there is an alternative treatment. Chondromalacia Patella Stages Four stages describe the severity of a runner’s knee, ranging from Stage 1 to Stage 4. The least severe stages are Stages 1 and 4, respectively. Depending on the degree, the cartilage in the knee is softening. Signals both abnormal surface characteristics and a softening of the cartilage. It is usually the beginning of tissue erosion. Shows active tissue deterioration and thinning of the cartilage. The most serious Stage is defined as the exposure of the bone and a sizable amount of deteriorated cartilage. There is likely bone-to-bone rubbing when there is bone exposure in the knee. Chondromalacia Patella Characteristics A dull, aching pain in the front of the knee is the most typical sign of patellofemoral pain syndrome. The following things can make it worse: Examination All four examination techniques—observation, mobility, feel, and X-ray—are used to assess the knee. Medical management Exercise and education are two of a treatment program’s most essential elements. Education enables the patient to fully understand their condition and the best ways to take care of it for a quick recovery. The appropriate structures, such as the gluteal muscles, quadriceps, and hamstrings, are lengthened and strengthened through exercises. The biodynamic structure of the patellae can be restored with acupuncture and fire needling, which can also help treat the clinical symptoms and signs of chondromalacia patellae. If conservative measures fail, a variety of surgical options are available. Two additional treatments that may be successful are: Only removing cartilage will not cure chondromalacia patellae. The biomechanical deficiencies, which must be addressed, can be managed using several techniques. Although there is no single method for treating chondromalacia, most medical professionals concur that non-surgical treatment is the best choice. Physical Therapy Management Exercise Program Physically, it is strongly suggested to use conservative treatment for chondromalacia patellae. Short-wave diathermy can assist in reducing discomfort and enhancing local blood flow, enhancing the nutrient supply to the articular cartilage. Care must be taken when organizing an exercise program. Examples of traditional therapeutic approaches include the following: The program should include both strengthening and stretching. Hamstring length and flexibility are lower in patients with patellofemoral pain syndrome than in those without symptoms. While stretching can improve knee flexibility and function, pain relief is not always immediately achieved. Another treatment method involves warm needling. Coupled with therapeutic exercises, it provides pain relief that lasts longer than warm needling and medication alone. Ice Medication The use of ice during an acute flare-up may help to reduce pain, but it should not be a long-term treatment option. NSAIDs may be useful for pain relief in the short term to resume normal knee function and mobility and begin an exercise regimen. Taping and Braces Although there is conflicting evidence, taping the patella to restrict its movement might provide some short-term relief. Many people use a method called “McConnell taping” or “kinesio taping.” Bracing the patella and knee joint is another method for reducing symptoms and pain. However, the patella’s tracking will be altered, and the quadriceps’ capacity for active contraction will be reduced. Bracing may be beneficial in the short term to give patients support and pain relief to prevent arthralgic movements and maintain a gait as close to normal as possible. Before and following surgery patients can wear braces before and after surgery, but the brace should allow for some variation in the pressure and medial pull on the patella. Physical therapy and the use of a patellar realignment brace are beneficial for patients with chondromalacia patellae. Foot Orthoses Foot orthoses are a different pain-relieving option, but they should only be considered when it is determined that improper lower limb mechanics are the root of knee pain. It might be the situation if Foam Roller Foam rolling can be beneficial by releasing tight muscles and relieving pressure on the patella. If you are searching for the best physiotherapist in Gurgaon, check out Gold Medal Physiotherapy. We recommend you visit the Gold Medal Physiotherapy and consult with the experts.

Your pelvic muscles lean excessively to one side, a common postural abnormality known as a pelvic tilt. This deficiency frequently appears when your pelvic muscles remain in the same position for an extended period. For instance, slumping on the couch or spending hours in a painful office chair may cause your pelvic muscles to adapt. The altered forces may alter your range of motion. If you have a pelvic tilt, you can treat it with specific exercises. Learn more about this postural weakness’ causes, symptoms, and treatments. What is pelvic tilt? The pelvis is essential to how the human body works. This region distributes your weight so that your lower limbs can move. Additionally, it helps maintain the position of the abdominal organs. Your pelvis should ideally not sag forward or backward while you are sleeping. A pelvic tilt can occur when the pelvic muscles are overextended or underused, which makes them pull in one direction. Pelvic tilts can be classified into two categories. Anterior pelvic tilt. Long-term sitting causes your hip flexor muscles to shorten, leading to this condition’s development. These tense muscles cause the pelvis to droop and tilt anteriorly or forward. Posterior pelvic tilt. Your pelvis tilts back due to the hip extensor shortening, which results in this deficiency. Lower back pain could result from posterior pelvic tilt. What actions might result in a pelvic tilt? The pelvic tilt is frequently brought on by: Due to extended periods of inactivity, many people develop pelvic tilt. According to a recent study, 19.7% of American adults spend more than eight hours per day sitting down, while 26.9% of adults in America spend more than four hours doing so. Sitting for extended periods can cause pelvic tilt and other posture problems. Importance of pelvic tilt Patients with chronic lower back pain (LBP) typically perform pelvic tilting exercises in the sagittal plane to realign their lumbar spines. A posture that encourages lumbar lordosis has been identified as one of the leading causes of LBP. The posture that causes lumbar lordosis must be reduced to treat LBP effectively. While posterior pelvic tilting has the opposite effect, anterior pelvic tilting strengthens lumbar lordosis. Rehabilitation frequently makes use of exercises that require posterior pelvic tilting. The local muscles, which also regulate motion in the pelvic sagittal plane, may be related to anterior and posterior pelvic tilting, suggests research. Local muscle training may help LBP patients achieve better lumbar alignment in the sagittal plane. Training the transversus abdominis and multifidus may be advantageous in patients with excessive lumbar lordosis and decreased lumbar lordosis. Chronic low back pain sufferers may have less control over their posture, decreased pelvic proprioception, and decreased “movement awareness.” It raises the question of whether certain positions or activities that require extreme movement (such as movement that is excessive or limited) may put people at risk for LBP. Anterior pelvic tilt An anterior pelvic tilt, also known as a change in posture, occurs when the front of the pelvis rotates forward, and the back of the pelvis rises. Some studies claim that up to 85% of men and 75% of women with no symptoms have an anterior pelvic tilt. An anterior pelvic tilt can be brought on by excessive sitting or inactivity. It affects posture and spine shape and may result in additional symptoms. Posterior pelvic tilt When the pelvis is misaligned and tilted at the back, this is known as a posterior pelvic tilt. It is caused by an unbalanced relationship between the legs’ muscles and the core’s powers, which is influenced by your anatomy, usual posture, and movement patterns. Numerous symptoms can appear, including a hunched posture, tight hamstrings, and back pain. In addition to modifying sitting and sleeping positions, exercises that target specific muscles are frequently used as treatment methods. A joint exercise for correcting pelvic tilt This exercise strengthens your abdominal muscles while stretching the muscles in your lower back. Because this exercise will help put your spine in the correct neutral position, keep track of your progress. What medical procedures does Gold Medal offer to correct pelvic tilt? We use manual techniques to realign the bones, such as MFR, osteopathy, postural exercises, dry needling, and manipulation and mobilization of the bones. Each patient receives a customized treatment plan from us that focuses on releasing tight muscles, strengthening weak muscles, modifying gait, and enhancing posture. If you face any Pelvic Tilt problems, you should check out Gold Medal Physiotherapy. They are among the best and provide the best Pelvic Tilt Treatment in Gurgaon.


Quality Treatment With Super Affordable Price
Call us anytime
